Introduction
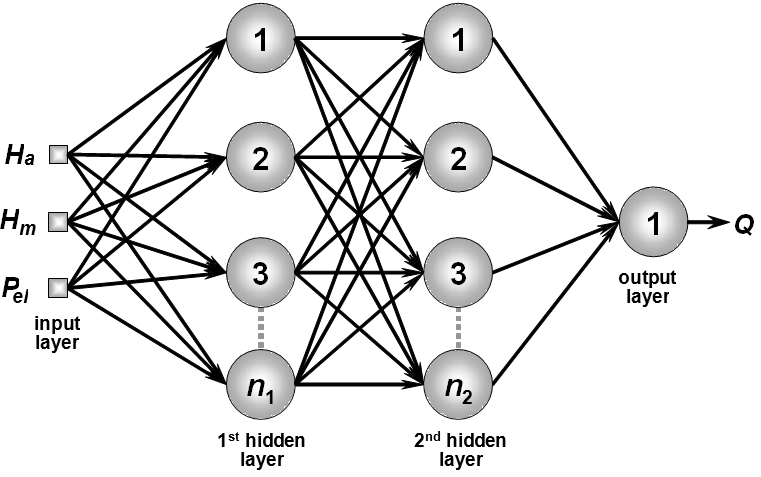
A multilayer perceptron (MLP) is a feedforward artificial neural network model that maps sets of input data onto a set of appropriate outputs. An MLP consists of multiple layers of nodes in a directed graph, with each layer fully connected to the next one. Except for the input nodes, each node is a neuron (or processing element) with a nonlinear activation function. MLP utilizes a supervised learning technique called backpropagation for training the network. MLP is a modification of the standard linear perceptron and can distinguish data that are not linearly separable.
The multilayer perceptron consists of three or more layers (an input and an output layer with one or more hidden layers) of nonlinearly-activating nodes and is thus considered a deep neural network.